The Ankura semi-weekly Cyber Threat Investigations and Expert Services (CTIX) FLASH Update is designed to provide timely and relevant cyber intelligence pertaining to current or emerging cyber events. The following is a collection of cyber threat intelligence leads assembled over the past few days and typically include high level intelligence pertaining to recent threat group/actor activity and newly identified vulnerabilities impacting a wide range of industries and victims. Please feel free to reach out to Flash (flash@ankura.com) if additional context is needed.
Ransomware Metrics Update
CTIX analysts compile threat activity data from a variety of sources including DarkFeed.io to track ransomware and data leak trends. Below are this week’s analytics compiled into a graph:
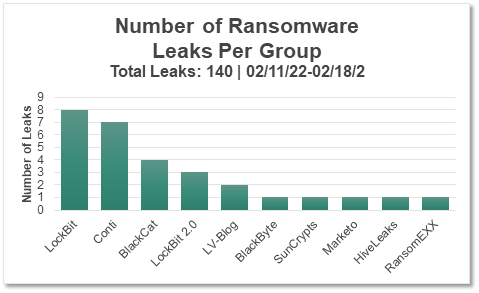
LockBit has surpassed Conti this week with eight (8) new leaks, followed by BlackCat (ALPHV) and LockBit 2.0 who totaled at four (4) and three (3) new leaks respectively. SunCrypts is also back this week accompanied with appearances from Marketo, HiveLeaks, and RansomEXX. This week has shown a drop in overall leaks compared to the last two (2) weeks, indicating a slight downtrend in ransomware attacks.
Ransomware/Malware Activity
Developing Botnet "Kraken" Utilizes Golang Programming Language
A new botnet has been discovered by threat intelligence firm ZeroFox utilizing the Golang programming language. The malware has named itself "Kraken" on its command-and-control (C2) server, not to be confused with the botnet from 2008 with the same name. It was originally created in October 2021 when a public GitHub repository using the name "tcp" was uploaded with files containing the first version of the malware. While ZeroFox could not confirm the threat actors running the botnet were responsible for the repository, it is clear this code was used in the development of the malware and pre-dates samples found in the wild. The botnet is installed almost exclusively through SmokeLoader, a malware loader that uses spam campaigns and exploit kits to spread. It is packaged alongside RedLine Stealer which is an extremely common piece of malware that exfiltrates credentials and cryptocurrency wallets back to the attacker. Once installed, it attempts to hide itself from Microsoft Defender using PowerShell commands. It then takes a screenshot of the desktop and runs RedLine Stealer to harvest common cryptocurrency wallets. At any moment, Kraken operators can arbitrarily run shell commands on the victim machine. The botnet has been shown to have up to 6,500 victims that generate an estimated $3,000 a month for the creators. Kraken is the newest malware to utilize Golang for its concurrency and other features. CTIX analysts are monitoring the development of this new botnet and will update for any new developments.
Wave of Attacks Identified Utilizing Microsoft Teams to Deploy Malware
Security researchers at Avanan, a Check Point company, have recently identified that threat actors are spreading malware through Microsoft Teams conversations. Avanan, in their report linked below, detailed that the thousands of attacks utilizing this vector began in January 2022 and that actors are compromising Microsoft teams accounts in order to drop malicious executable files, specifically a file called "User Centric" in the sample provided. The actor can compromise the accounts in various ways, such as exfiltrating credentials for email, or Microsoft 365 through phishing campaigns, or the compromise of a targeted company's partner organization. The "User Centric" trojan then writes data to the Windows registry, installs dynamic-linked libraries (DLLs), creates shortcut links to self-administer, sustains presence, and fully compromises the end-user's machine. This technique is notable to researchers due to the "inherent trust of the platform" (Microsoft Teams) that users have. The report explained, "Most employees have been trained to second-guess identities in email, but few know how to make sure that the name and photo they see in a Teams conversation are real." The researchers emphasized that this wave of attacks utilizing Microsoft Teams conversations demonstrate that "hackers are beginning to understand and better utilizing Teams as a potential attack vector".
Security Researchers Publish Whitepaper Claiming to Recover 95% of Data Encrypted with Hive Ransomware
A team of South Korean security researchers from Kookmin University in Seoul have published a whitepaper financially supported by a grant from the Korean government and Korea’s Information Security Agency (KISA), that details known exploitable vulnerabilities in the Hive Ransomware encryption algorithm. The techniques detailed in the paper claim that in their experiments they were able to recover approximately 95% of the master key used to encrypt the drive, without having access to the attacker's private RSA key. This method allowed them to recover 82% to 98% of the encrypted drive's data. In the past, Hive ransomware, which first appeared in June 2021 has been so devastating to multiple organizations, that the FBI had to issue an alert for it. Along with encrypting a drive or network of drives for ransom, this group applies pressure to their victims by threatening to leak the data on their HiveLeak dark web site. If the methods laid out in the report are sound, this could change the way ransomware is perceived as a threat by victims and would empower them to take immediate actions other than paying the ransom to save their data. Currently, researchers from both Bitdefender and Kaspersky are reverse engineering the methods detailed in the paper to create a free Hive Ransomware decrypter. The Ankura CTIX will continue to monitor this unprecedented matter, and updates will be published as more details arise.
Nation-State Activity
Threat Insight: TA2541
TA2541 is an emerging threat actor whom targets aviation, aeronautical, aerospace, manufacturing, and defense industries and has been active in-the-wild since 2017. This cybercriminal commonly deploys numerous remote access trojans across organizations throughout these industries via social engineering tactics. Within these emails, themed after transportation services like aircraft, yacht, and charters, malicious RAR executables are attached which allow for an outbound connection to a threat actor controlled command-and-control (C2) server where additional payloads are downloaded to the victim's device. Payloads from this threat actor include the AsyncRAT, a malicious program capable of communicating over an encrypted connection harvesting system information, relaying keylogger information, and establishing persistence on the system. TA2541 has been observed utilizing other remote access trojans including NetWire, WSHRAT, and Parallax. On average, these threat actors will disperse thousands of emails to targeted organizations to employees regardless of corporate hierarchy. The amount of compromised victims tied to this threat actor is currently unknown, but is believed to still be targeting companies within these industries and will do so in the future.
Iranian Cyber Activity; Subjected To Monthly Attacks By Numerous Threat Groups
In recent months Iran has been overwhelmed by cyberattacks from threat actors worldwide. The most significant of these attacks occurred in January where the Iranian state broadcaster IRIB fell victim to threat actors who broadcasted footage of foreign leaders calling for an assassination of the supreme leader. However, there were several other cyberattacks that lead up to this point. In July 2021, threat actors targeted Iranian national cargo and railway services which delayed transit of viable goods across the region. Later in August, Tapandegan threat actors leaked CCTV footage from inside the Evin prison, revealing video of prisoners being abused by their captors. In October another threat group cripples the nations fuel supply availability by disrupting electronic payment platforms used to purchase fuel. When customers tried to purchase fuel at a gas station, upon swiping their card the phone number of the Supreme Leader appeared on the screen, mocking the regions government control and their officials. Since October 4 more attacks have occurred against the Iranian state including two national television disruptions, an airline attack, and more prisoner footage from inside Ghezel Hessar Prison displaying further abuse of prisoners. With rising geopolitical issues and Iran consistently being targeted month after month, analysts believe there will be more attacks on the horizon against the country with several threat groups joining in to give their fair share. CTIX is continuing to monitor the situation and will provide additional updates accordingly.
Vulnerabilities
Adobe Out-of-Band Bulletin Updated to Reflect Mitigations for a Second Critical Vulnerability
UPDATE: Adobe has added a new critical zero-day vulnerability to their out-of-band security bulletin and update released last week. This new flaw is tracked as CVE-2022-24087, and is also an improper input validation flaw, that if exploited would allow unauthenticated attackers to perform remote code execution (RCE) on e-commerce websites employing Adobe's vulnerable Commerce and Magento Open-Source instances. This exploitation would enable an attacker to steal customer payment information. The original bulletin from last week was for CVE-2022-24086, a vulnerability that had already been exploited in-the-wild at the time. Adobe patched the CVE-2022-24086 flaw however, it was patched inadequately, and as of February 17, 2022, security researchers from the Offensive Team at Positive Technologies tweeted proof that they have developed a reliable exploit that bypasses the patch and leads to the same RCE in multiple ways. Although these are both critical zero-day flaws, Positive Technologies has provided the context that these exploits are especially difficult to execute correctly, and that even the original flaw (CVE-2022-24086) had only been exploited a handful of times by very sophisticated hackers. Adobe has stated, "We have discovered additional security protections necessary for CVE-2022-24086 and have released an update to address them (CVE-2022-24087)." It is imperative for any site administrators and owners leveraging either of these products to update to the most secure version as soon as possible. The Ankura CTIX will continue to monitor this situation and will update our readers with more information if necessary.
Emerging Technology
Privacy Sandbox Initiative Announced for Android
Google has announced that they will be bringing their Privacy Sandbox initiative to Android. The Privacy Sandbox is a conglomerate of different technologies that will stifle covert tracking with cookies and digital fingerprints, by limiting the amount of user, ad, and device data collected by third parties. The Privacy Sandbox will be similar to Apple's App Tracking Transparency (ATT) framework; however, this initiative will require much less explicit authorization from the user than the ATT framework. ATT requires that the user authorizes or denies instances of tracking as they make contact with those services across the web. The Sandbox Initiative will place users into five (5) rotating weekly categories with three (3) subset categories based on their browsing activity, so instead of being targeted by all advertisers via cookies, a user will be targeted by relevant companies who correlate with the user's actual interests. This technology would create archetypes depending on the user, which would require less direct authorization due to the technology cataloging what is and isn’t in-line with the user’s interests. Ultimately, this initiative aims to better protect user privacy, deliver better targeted ads, while still being able to provide Google browsing services free of cost. Google has announced they plan to field a beta version of this technology by the end of the year, while aiming to release the completed initiative within three (3) years. The Ankura CTIX will continue to report on the latest technologies, painting a picture of the future for our readers.



