Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has irrevocably altered the economic landscape in Europe. With sanctions serving as the weapon of choice for western powers, the constant flux of new entities and individuals, as well as regulations, increases risk to companies conducting their business in the global marketplace. The broad range of sanctions regimes contemplated by the Biden administration, from sectoral sanctions targeting energy and finance to the designation of state-owned enterprises and prominent Russian individuals, will be in full effect within the next few days. In addition to OFAC sanctions from the Department of Treasury noted above, the Department of Commerce listed 49 Russian businesses on its Entity List in response to the aggression against Ukraine. This listing limits Russian access to critical technologies, including microelectronics, telecommunications devices, sensors, avionics, navigation, and marine equipment. [4]
The EU similarly imposes restrictive measures (including sanctions) either to implement UN Security Council resolutions or on its own initiative to achieve the goals of the common foreign and security policy such as promoting international peace and security. The Council of the EU passes resolutions on the adoption, extension or repeal of sanctions regimes which enter into force as soon as they have been published in the Official Journal of the EU. Given the fluid situation on the ground, the EU has demonstrated a remarkable deftness in coming to a resolution on new sanctions and their implementation.
For its part, Russia has removed corporate registries and other publicly available information, making a murky business environment even more opaque. Having lived with western restrictions since the 1990s, Russia is prepared to both weather the direct impact of sanctions, as well as utilize novel financial systems, such as a "digital ruble" cryptocurrency, to evade those sanctions. [5]
Key Takeaways
- Initial sanctions activity against Russian entities, including financial institutions and government-linked individuals, demonstrates the breadth and depth of the new sanctions landscape with which companies will have to contend. As an example, Sberbank alone has 25 subsidiaries, which will require research, screening, and risk mitigation.[1]
- In response to the Russian incursion, the Department of Treasury's Office of Foreign Asset Control (OFAC) recently leveraged Directive 2 under Executive Order 14024, which prohibits:
- the opening or maintaining of a correspondent account or payable-through account for or on behalf of any entity determined to be subject to the prohibitions of the Russia-related CAPTA Directive, or their property or interests in property; and
- the processing of transactions involving any such entities determined to be subject to the Russia-related CAPTA Directive, or their property or interests in property. [2]
- Similarly, the European Union agreed on sanctions through Council Regulation (EU) 2022/263 on February 23, 2022, targeting 27 individuals and entities for their actions against territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine, the 351 Russian Duma members who voted for the recognition of Donetsk and Luhansk, as wells as imposing restrictions on economic relations with those regions.
- On February 24, 2022, the European Commission published a press release announcing yet another package of sanctions, aimed at blocking Russian access to technologies and markets, as well as freezing Russian assets in the European Union and preventing access of Russian banks to European financial markets.
- The pressure on Russian financial systems is rising steadily. In a joint statement published on February 26, 2022, the leaders of the US, UK, EU announced their commitment to ensuring that selected Russian banks would be removed from the SWIFT secure electronic financial system which allows participants to conduct transfers worldwide. This will have significant implications for international companies seeking to invest, remit payments, and otherwise conduct business with Russia. [3]
- The issues identified in this alert are current as of February 28, 2022. Given the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, and the accompanying geopolitical maneuvering, Ankura will provide updates based on developments in sanctions activity.
How the sanctions environment will impact companies
Sanctions violations are unique in their impact across multiple facets of business operations. Not only do they significantly affect a company’s bottom line, often in the millions of dollars, sanctions can also disrupt supply chain operations, damage a company’s competitive edge, and create uncertainty with customers and clients.
There are four significant categories of risk assumed by a business which are directly addressed through the design and implementation of a sanctions compliance program. The more robust a sanctions compliance program, the more likely it is that not only will violations be avoided, but also that regulators would recognize good-faith compliance efforts when evaluating any breaches of sanctions in the future.

How Ankura Can Help
During times of uncertainty, it is important to have a partner who can provide a vast array of services, with a tailored approach to each client's specific needs.
Ankura provides a full-scale menu of options to identify possible sanctions exposure, properly scope and scale a sanctions program, and assist in mitigating risk. Ankura also clearly documents the identified risks, the correlating controls, and the test results which validate the effectiveness of a sanctions screening program. Ankura can also provide tailored screening solutions to enable both forward-leaning and lookback historical capabilities. This end-to-end approach allows Ankura to serve as a full-spectrum sanctions compliance solution, maintaining seamless business operations while keeping pace with a constantly shifting regulatory environment.
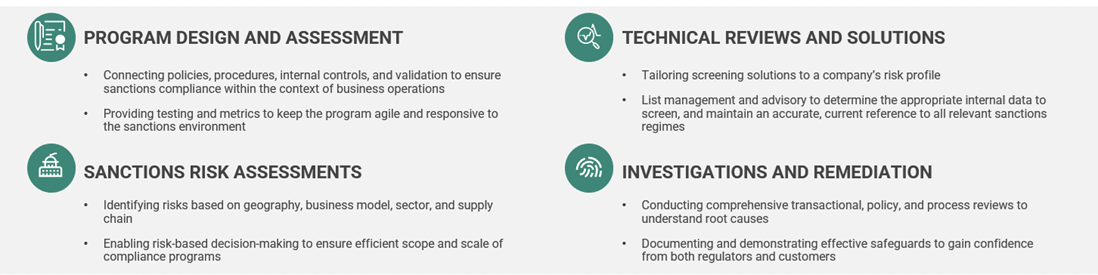
Ankura leverages a truly global reach to provide both immediate, on-ground response to client needs and tailored, regional expertise. Our team consists of seasoned former government regulators, financial crimes investigators, and technical subject matter experts capable of addressing all facets of a company's sanctions risk profile.

[1] LinkedIn, FiveBy Solutions Summary
[2] Homeland Security Today, "New Sanctions: Top Ten Russian Financial Institutions Now Under U.S Restrictions"
[3] EU STATEMENT/22/1423 "Joint Statement on further restrictive economic measures"
[4] Wired, "How US Sanctions Will Crimp Russia's Tech Sector"
[5] The New York Times, "Russia Could Use Cryptocurrency to Blunt the Force of U.S. Sanctions"
© Copyright 2022. The views expressed herein are those of the author(s) and not necessarily the views of Ankura Consulting Group, LLC., its management, its subsidiaries, its affiliates, or its other professionals. Ankura is not a law firm and cannot provide legal advice.



